What Are AI Agents? More Than Just Chatbots
What are AI Agents?
Introduction
-
When ChatGPT was launched on November 30, 2022, it revolutionized AI by enhancing computers' ability to understand and communicate in human language.
-
Every AI application relies on an AI model to perform its tasks. Think of AI models as interns in a company initially, they make mistakes, but with guidance from peers and mentors, they improve over time. As interns gain skills, experience, and knowledge, they learn from their mistakes and evolve into responsible professionals. Similarly, AI models learn from data, user feedback, and various experiences, gradually enhancing their performance and accuracy.
- An AI model is a tool that learns from examples and helps us solve problems or complete tasks more efficiently.
-
Since the launch of ChatGPT, AI models have evolved significantly. OpenAI's GPT-4o and Google's Gemini 2.0 now demonstrate reasoning abilities comparable to a PhD graduate. Meanwhile, Meta and Mistral have developed powerful open-source models with impressive reasoning capabilities. DeepSeek R1, another open-source model, has even shown the potential to outperform some of OpenAI's offerings.
-
Moore's Law is the observation that the number of transistors on an integrated circuit will double every two years with minimal rise in cost. In the case of AI models, we are seeing breakthroughs every 6 months.
-
AI models are getting bigger, more accurate and more cost-effective.
- We are seeing a great evolution of AI models in Text. AI models are also evolving in Image, Video and Audio.

- In past our AI models could detect multiple objects.
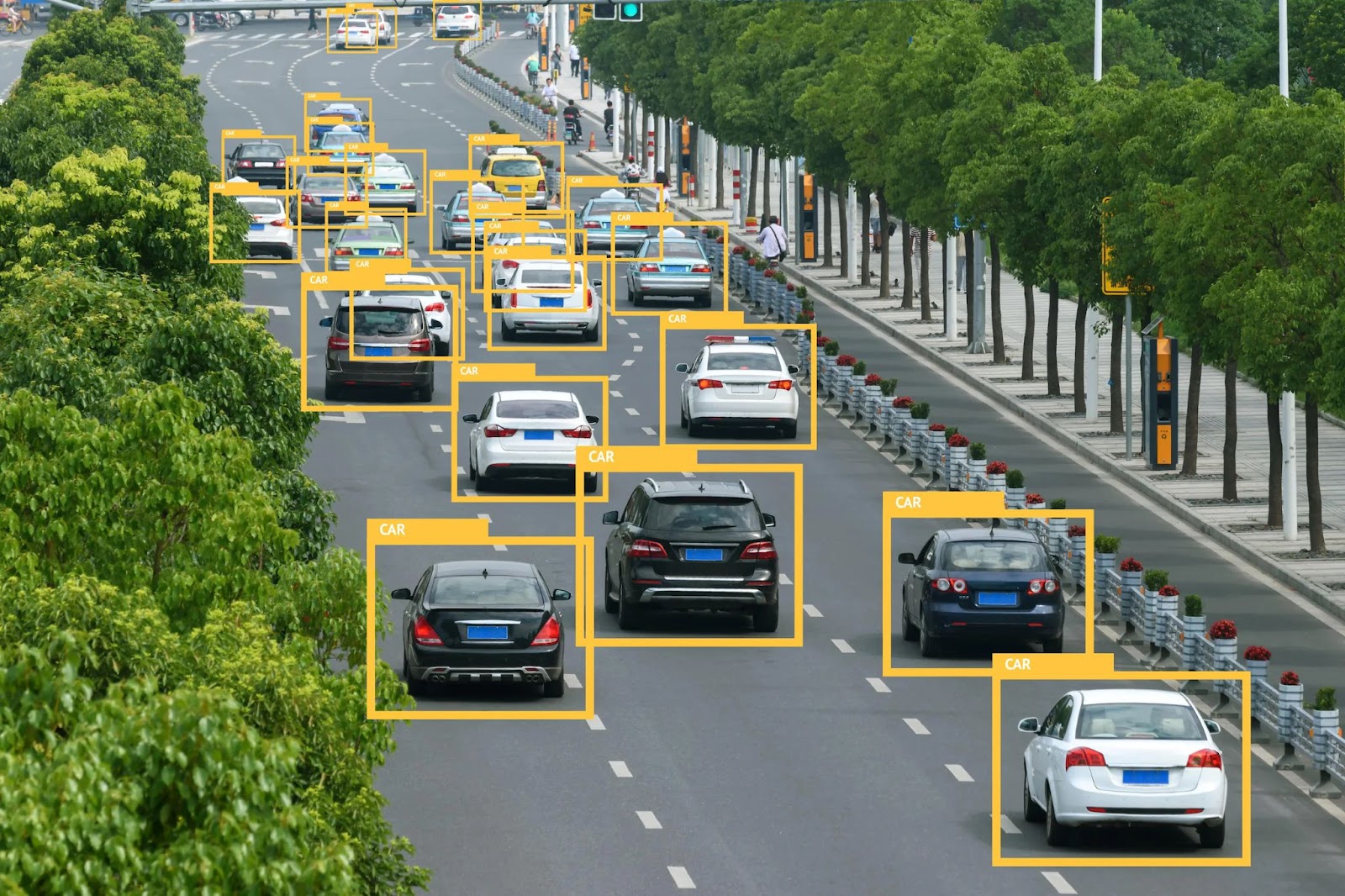

- Now our AI models are capable of identifying much more than just objects.

- Previously, if I open our website digiqt.com it will be seen by AI model as follows,
- Now, AI models see websites just like humans.

-
As AI models continue to evolve, why not leverage them to handle our tasks? AI agents, like human agents, excel in specific areas of expertise.
-
Consider a company employing a market research analyst responsible for analyzing the industry and developing business reports on opportunities and risks. As a human, the analyst conducts thorough research by gathering data from multiple sources such as Gartner, research papers, industry news, websites, videos, and podcasts. After compiling relevant insights, they create a comprehensive business report covering opportunities, risks, case studies, and geographical market details.
- AI agents can efficiently handle all these tasks without human intervention. They can gather data from various sources, analyze industry trends, and generate comprehensive business reports, including opportunities, risks, case studies, and geographic insightsautomating the entire process with speed and accuracy.
AI Agents
-
AI Agents are intelligent computer applications that perform tasks without human assistance towards a goal.
-
AI agents are software entities capable of making autonomous decisions and performing tasks with minimal or no human intervention.
-
For example, an AI agent acting as a market research analyst can follow a structured workflow, executing each step sequentially. It can conduct keyword-based searches on search engines, gather industry reports, explore blogs, listen to podcasts, analyze YouTube videos, and finally compile a comprehensive report by integrating insights from all these sources.
-
AI Agent environment refers to everything an AI agent interacts with while performing its tasks. It consists of the external conditions, data sources, tools, and constraints that influence the agent’s decision-making and actions. The environment provides inputs to the AI agent and receives outputs in response to the agent’s actions.
-
These agents use AI Models to interact with their environment, learn from data, and optimize their performance over time.
-
In the above market research analyst agent example, search engines, Industry Reports & Data Sources, YouTube, podcasts, blogs and articles are the environment.
-
Another example can be, Imagine you need statistical data about the insurance market but don’t have the time to conduct research and organize the information into a table. This is where AI agents come in. Instead of manually searching for data, you can simply enter a query like, "I need statistics on the insurance market." The AI agent will then research relevant information from various sources, summarise the key insights, and present the data in a structured format—saving you time and effort.
-
Every process can be re-imagined with AI agents.
How Do AI Agents Work?
- AI agents follow a structured process known as the Perceive-Think-Act-Learn cycle. This allows them to gather data, make intelligent decisions, execute actions, and continuously improve.
1. Perception (Data Collection & Input Processing)
- The AI agent collects data from various sources such as customer interactions, emails, CRM systems, sales reports, IoT devices and any other data source.
- The data can be in the form of text, video, audio, images, structured/unstructured records, or real-time analytics.
- We will understand this from the example use case. A powered Sales Agent will handle inquiries from customers. Similar agents can be built for any other processes.
Example (Business Use Case: AI-Powered Sales Agent)
- A company uses an AI-driven sales assistant to analyze customer inquiries from emails and chat messages.
- The AI scans an incoming email:
- Customer: "We are interested in purchasing 500 units of your product. Can you share pricing details?"
- The AI extracts key details like product quantity, inquiry type, and urgency level.
2. Decision-Making (Processing & Intelligence)
- The AI processes the collected data using AI models and business logic to determine the best response.
It can predict customer intent, prioritize leads, and suggest personalized offers.
Example (AI-Powered Sales Assistant)
- The AI analyzes past interactions with this customer from CRM and recognizes them as a repeat buyer.
- Based on previous order history and company policies, it determines that a 10% discount can be offered for bulk purchases.
- The AI prioritizes this inquiry as urgent and drafts an appropriate response.
- All of the above logic can be done with the help of AI prompts.
3. Action Execution (Performing the Task)
- Based on its decision, the AI Model will instruct the application to execute an action, which may include sending an email, updating CRM records, or alerting the sales team.
Example (AI-Powered Sales Assistant)
- The AI automatically drafts an email to the customer:
- "Dear [Customer Name],*
Thank you for your inquiry! For bulk orders of 500+ units, we offer a 10% discount. Your total cost will be $X. Let us know how you’d like to proceed."*
- "Dear [Customer Name],*
- The AI updates the CRM system with the lead status and notifies the sales team about the potential deal.
4. Learning & Optimization (Improving Over Time)
- AI agents continuously learn from interactions, feedback, and outcomes to improve their accuracy and efficiency.
Example (AI-Powered Sales Assistant)
- If the customer negotiates for a higher discount, the AI records this behaviour and learns to suggest better pricing strategies in the future.
- If the response time affects deal closure rates, the AI optimizes its workflow to prioritize similar leads faster in upcoming interactions.
- Over time, the AI becomes more personalized and efficient in handling customer inquiries, leading to higher conversion rates and improved customer relationships.
What are the use cases of AI agents in different industries?
- With AI Agents, any human-led process can be reimagined and optimized through automation and intelligence.
AI agents are revolutionizing multiple industries:
- Healthcare – AI-powered diagnostic tools, virtual health assistants, and robotic surgeries.
- Finance – Fraud detection, algorithmic trading, and AI-driven customer service chatbots.
- Retail & E-commerce – Personalized recommendations, inventory optimization, and automated customer support.
- Manufacturing – Predictive maintenance, smart automation, and supply chain optimization.
- Marketing & Advertising – AI-powered content creation, targeted marketing campaigns, and customer sentiment analysis.
- Autonomous Vehicles – AI agents enable self-driving cars to make real-time navigation decisions.
What are the risks associated with AI agents?
1. Bias & Discrimination
-
AI models learn from historical data, which may contain inherent biases.
-
If training data is biased (e.g., gender, race, socioeconomic background), AI can reinforce and amplify discrimination.
-
Example: AI-powered recruitment tools may unintentionally favor male candidates if trained on historical hiring patterns where men were preferred.
Risk Impact:
-
Can lead to unfair treatment in hiring, banking, law enforcement, and healthcare.
-
AI decisions may be difficult to audit, making bias hard to detect and correct.
-
Mitigation: Use diverse and unbiased training data, conduct regular audits, and implement fairness guidelines.
-
Reinforcement Learning (RL) is gaining traction as a powerful approach, with models like Deepseek R1 built on this framework. RL works like teaching a child through trial and error an AI experiments with different actions, receives rewards for good choices and penalties for bad ones, and gradually improves its decision-making over time.
2. Security Threats & Cyber Attacks
- AI systems can be hacked, manipulated, or exploited by cybercriminals.
A. Jailbreaking Attacks
- Prompt Injection – Tricking the model into bypassing safety filters.
- DAN (Do Anything Now) Attack – A famous jailbreak method to make LLMs ignore ethical constraints.
- Reverse Prompt Engineering – Extracting hidden or confidential data by manipulating responses.
- Token Smuggling – Breaking up or obfuscating restricted words to bypass content moderation.
B. Adversarial Attacks
- Gradient-based Adversarial Attacks – Generating adversarial text to force misclassification.
- Text-based Adversarial Perturbation – Modifying words slightly (e.g., adding typos or spaces) to trick the model.
- Universal Adversarial Triggers – Embedding specific words or phrases that cause unwanted behavior in LLMs.
C. Data Poisoning Attacks
- Backdoor Attacks – Training the model with hidden patterns that trigger specific malicious behaviors.
- Label Flipping Attack – Poisoning training data by assigning incorrect labels.
- Semantic Poisoning – Manipulating LLMs by injecting biased or misleading information into training datasets.
D. Model Extraction & Theft
- Model Inversion Attack – Extracting sensitive data from an LLM’s responses.
- API Extraction Attack – Querying an LLM excessively to replicate its behavior and reconstruct the model.
- Membership Inference Attack – Determining whether specific data was used in the training set.
E. Social Engineering & Manipulation
- Persuasion Attacks – Using LLM-generated content to manipulate opinions or spread misinformation.
- Sockpuppet Attacks – Using AI to generate fake identities for mass influence.
- Automated Phishing – Generating deceptive emails or messages for scams.
- Example: Hackers can manipulate self-driving cars by altering street signs, causing misinterpretation and dangerous driving behaviors.
Risk Impact:
-
AI-based fraud detection can be bypassed by adversarial attacks.
-
AI-powered deepfakes can spread misinformation, fraud, or identity theft.
-
Mitigation: Use robust cybersecurity measures, AI model validation techniques, and adversarial testing.
3. Data Privacy & Ethical Concerns
-
AI agents require vast amounts of data, raising concerns over privacy and unauthorized data usage.
-
Companies using AI must comply with regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA to protect user data.
-
Example: AI-based voice assistants (like Alexa or Siri) continuously listening to conversations can lead to privacy breaches.
Risk Impact:
-
Unauthorized access to sensitive information (e.g., financial records, medical data).
-
User trust declines when AI misuses personal data.
-
Mitigation: To secure Large Language Models (LLMs) from adversarial attacks, here are key prevention strategies for each type of hacking technique:
-
Guardrails are emerging as a powerful solution to mitigate these risks. There are open source guardrails like NeMo Guardrails (by NVIDIA), TruLens, Meta AI’s Llama Guardrails, AWS Bedrock Guardrails and many more. Guardrails are security and compliance frameworks designed to protect AI models from misuse, adversarial attacks, and unsafe outputs. They ensure that AI operates within ethical, legal, and security boundaries.
A. Preventing Jailbreaking Attacks
- Robust Prompt Filtering – Implement advanced prompt moderation to detect and block adversarial inputs.
- Dynamic Context Awareness – Use context-based filtering to prevent prompt injections and DAN-style attacks.
- Rate Limiting – Restrict excessive queries to prevent iterative jailbreak attempts.
- Reinforcement Learning with Human Feedback (RLHF) – Fine-tune models to resist manipulation.
B. Preventing Adversarial Attacks
- Adversarial Training – Expose the model to adversarial inputs during training to improve robustness.
- Text Normalization – Remove typos, special characters, and hidden encoding tricks to stop token smuggling.
- Input Validation – Flag and sanitize suspicious inputs before processing them.
C. Preventing Data Poisoning Attacks
- Secure Training Data Pipelines – Ensure only verified, high-quality datasets are used for model training.
- Anomaly Detection – Continuously monitor for inconsistencies or injected biased content.
- Differential Privacy – Prevent the model from memorizing sensitive data during training.
D. Preventing Model Theft & Extraction
- Query Rate Limits – Prevent excessive API requests to avoid model extraction.
- API Monitoring – Detect and block repeated, structured queries aimed at stealing model outputs.
- Encrypted Model Weights – Use cryptographic techniques to secure LLM internals.
- Watermarking AI Outputs – Embed invisible markers in responses to track unauthorized usage.
E. Preventing Social Engineering & Manipulation
- Bias & Misinformation Detection – Implement real-time fact-checking for generated content.
- Content Moderation & Logging – Monitor AI-generated text to flag potential phishing, scams, or persuasion attempts.
- User Authentication – Require authentication for sensitive AI responses to prevent abuse.
- Securing an LLM requires a multi-layered defense, including input filtering, adversarial training, secure APIs, and continuous monitoring. Would you like me to expand on any specific prevention method?
4. Ethical Dilemmas & Moral Responsibility
-
AI agents can face moral and ethical challenges, especially in critical areas like autonomous vehicles, healthcare, and military applications.
-
Example: In a self-driving car accident scenario, should the AI prioritize the passenger’s life or pedestrians' lives?
Risk Impact:
-
Raises legal and ethical debates about AI’s role in life-and-death situations.
-
Lack of a universal ethical framework for AI decision-making.
-
Mitigation: Establish global AI ethics standards, and ensure human oversight in AI-driven decisions.
What are the challenges and limitations of AI agents?
- Despite the rapid advancements in AI, AI agents still face several challenges and limitations that hinder their widespread adoption and effectiveness. These challenges range from technical issues to ethical and operational concerns.
1. Data Quality & Availability
- Data is essential to AI Model’s decision-making and training processes. Inaccurate results, however, may arise from incomplete, biased, or low-quality data. Getting high-quality, diversified, and well-labelled datasets is a challenge for many firms.
For instance, if trained on skewed or out-of-date data, an AI Agent can have wrong outcomes. For AI to work well, high-quality, real-time data must be available.
Modern AI models are having real-world data and it can be provided as context and the model can be fine-tuned with the help of new data to improve it.
2. High Development & Implementation Costs
- It takes a significant investment in infrastructure, processing capacity, and qualified personnel to develop and implement AI agents. Large AI model training requires high-performance GPUs, which can be costly.
Deepseek R1 can do better reasoning at the 90% cheaper cost. Modern developments in AI Model can reduce the cost over time.
Services like AWS Bedrock and OpenAI offer a pay-as-you-go model, allowing businesses to leverage their infrastructure instead of investing in costly in-house setups.
3. Explainability & Lack of Transparency
- Many AI models, particularly deep learning networks, operate as "black boxes," making their decision-making process difficult to interpret. This lack of transparency is a major issue in critical sectors like finance, healthcare, and law enforcement. For example, if an AI-based loan approval system rejects an applicant, it may not provide a clear reason, raising concerns about fairness and accountability.
AI development is happening in explainable AI. Tools such as Captum, Google’s Explainable AI (XAI) Tools, Fiddler AI etc can help in understanding AI model’s decision-making process.
4. AI Bias & Unintended Discrimination
- AI systems are trained on historical data, which may include racial, gender, or socioeconomic biases. AI agents have the potential to increase prejudice in employment, policing, and credit approvals if they are not properly supervised. For example, if the dataset had historically biassed towards males, an AI recruiting tool trained on previous resumes may favour male applicants. To lessen this problem, diversified training data and frequent bias checks are required.
Tools such as Truelens, Google Cloud’s Explainable AI, Microsoft Fairlearn etc can be helpful in AI bias detection.
5. Generalization & Context Understanding
- AI models provide responses with a confidence score, where a higher score indicates greater certainty in the answer. However, LLMs can sometimes generate incorrect answers with high confidence due to contextual misunderstandings or limitations in reasoning.
- Reinforcement Learning (RL) is proving effective in addressing these issues. Notable case studies include Two.ai and Deepseek R1, which demonstrate RL’s impact on improving response accuracy and contextual understanding.
What are the different types of AI agents?
1. Simple Reflex Agents
- Reflex refers to an instant reaction to an input without thinking or learning.
- These AI agents operate on predefined rules and respond instantly to environmental inputs without learning from past experiences. They use if-then logic to make decisions based on current conditions. These are basic rule-based agents and without any AI model’s intelligence.
Process Flow
- Sense the environment (Collect input data)
- Match condition to rule (Check if predefined rules apply)
- Perform action (Execute a response based on the rule)
- Repeat (No memory or learning involved)
Example: A thermostat turns on heating if the temperature drops below 18°C.
2. Model-Based Reflex Agents
- Unlike simple reflex agents, these agents maintain an internal model of their environment, allowing them to store past states and refine decision-making. States are history. This makes them more effective in changing environments
Process Flow
- Sense the environment (Collect input data).
- Update the internal model (Store previous states for reference).
- Match the rule using the model (Use stored knowledge to refine the decision).
- Perform action (Execute optimized response).
- Update the model for future use.
Example: A robotic vacuum cleaner maps a room to clean efficiently.
3. Goal-Based Agents
- These agents work towards a specific goal and choose actions that bring them closer to achieving it. They evaluate multiple possible paths and select the best course of action.
Process Flow
- Sense the environment (Gather current data).
- Identify the goal (Define the objective).
- Evaluate possible actions (Use algorithms to find the best path to achieve the goal).
- Choose the optimal action.
- Execute action (Move towards the goal).
- Repeat until the goal is achieved.
- Example: Google Maps calculates the fastest route based on traffic conditions.
4. Utility-Based Agents
- These agents maximize overall utility or efficiency, not just achieve a goal. They consider multiple factors like cost, time, and risks to determine the best possible action.
Process Flow
- Sense the environment (Gather real-time data).
- Define the objective (Set the desired outcome).
- Evaluate all possible actions (Consider cost-benefit analysis).
- Compute utility score (Measure each action’s effectiveness).
- Choose the action with the highest utility.
- Execute the action and refine future strategies.
- Example: AI-powered stock trading systems analyze market trends to maximize profits.
5. Learning Agents
- These agents improve over time by learning from their past experiences using AI algorithms. They analyze their previous actions, refine decision-making models, and become smarter with continued use.
Process Flow
- Sense the environment (Collect input data).
- Analyze past actions (Compare results with previous outcomes).
- Update the learning model (Adjust AI behaviour based on new data).
- Select the best action (Use improved knowledge for decision-making).
- Execute action and store the results.
- Repeat for continuous improvement.
- Example: AI chatbots like ChatGPT, Gemini and Deepseek refine responses based on user interactions.
6. Multi-Agent Systems (MAS)
- These involve multiple AI agents working together, either in cooperation or competition, to solve complex problems. They communicate, share knowledge, and coordinate actions.
Process Flow
- Sense environment (Each agent collects data).
- Communicate with other agents (Share knowledge).
- Decide action collectively (Agents collaborate or compete).
- Execute tasks in coordination.
- Update strategy based on group learning.
- Example: AI-powered traffic management systems optimize signals to reduce congestion.
7. Hybrid AI Agents
- These agents combine different AI techniques to create a more adaptive, intelligent, and efficient system. They integrate reflex actions, learning capabilities, and goal-based decision-making to enhance performance.
Process Flow
- Sense the environment (Gather multi-source data).
- Store data in memory (Use model-based learning).
- Define the goal & evaluate the best path (Goal-based decision-making).
- Compute utility score (Optimize actions for maximum benefit).
- Use learning mechanisms to improve future responses.
- Execute the best possible action.
Example: Self-driving cars use hybrid AI for obstacle detection, route optimization, and learning from past driving experiences.
How can you implement AI Agents in your company?
1. Define Objectives
- Identify what AI agents should achieve, such as automation, cost reduction, or better decision-making.
- Align AI goals with business strategy and long-term objectives.
- Focus on high-impact areas where AI can add the most value without considering other factors like cost, feasibility, risk etc.
- Focus on AI applications that provide measurable business value.
2. Assess Readiness
- Evaluate the availability and quality of data needed for AI.
- Review existing technology infrastructure for AI compatibility.
- Identify skill gaps and consider upskilling or hiring AI talent.
- Ensure organizational culture is open to AI adoption.
- Identify Risks such as compliance, security, financial etc.
3. Develop a Strategic Plan
- Start with small pilot projects to test feasibility.
- Set realistic timelines, milestones, and performance indicators.
- Allocate budget and resources for AI implementation.
- Plan for phased deployment to minimize disruptions.
- Plan for employee training, cultural shifts, and expert sessions.
4. Identify and Prioritize Use Cases
- Automate repetitive tasks such as data entry, scheduling, and customer support.
- Use AI for decision support in analytics, forecasting, and risk assessment.
- Showcase AI agent's capabilities across departments and encourage leaders of departments to come up with use cases.
- Improve process automation in HR, sales, finance, and IT.
- Check industry reports from Gartner, Statia, McKinsey etc. for how AI agents are being adapted.
- Conduct competitor surveys.
- How players in other geographies around the globe are leveraging AI agents.
5. Choose the Right AI Agents
- Deploy goal-oriented AI for handling more complex queries and workflows.
- Implement adaptive AI for learning and improving over time.
- Consider autonomous AI for decision-making with minimal human intervention.
- Choose the right AI Model and environment. The multi-model and Multi-Agent approaches can be used for better results.
6. Select AI Technologies and Models
- Identify the specific use cases and tasks for the AI agent.
- Evaluate industry benchmarks for AI models to understand their capabilities.
- Select the best AI model based on the required operations.
- Consider that different AI models have varying strengths—some excel at reasoning, others at mathematical computations.
- Explore industry-specific AI models that are optimized for specialized tasks.
- Choose open-source models and host them on private infrastructure if working with proprietary or Personally Identifiable Information (PII) data.
- Determine if any fine-tuning is needed for the selected model.
- Evaluate key factors such as model response time, cost, context length (tokens/words that can be processed), model architecture, and parameters.
- Balance evaluation factors to optimize performance and cost efficiency. If a lower-cost model meets the requirements, prioritize it. If a faster response time is needed, choose a smaller, optimized model.
7. Integrate AI with Existing Systems
- Connect AI agents with CRM, ERP, HR, and IT systems for smooth operations.
- Ensure data flows seamlessly between AI tools and company databases.
- Use APIs to enable AI-driven automation across business processes.
- Monitor integration for performance and security compliance.
8. Establish AI Governance and Compliance
- Define ethical guidelines to prevent bias and ensure fairness.
- Adhere to regulatory compliance standards for data protection.
- Maintain transparency in AI decision-making processes.
- Regularly audit AI systems for accuracy and risk management.
- Integrate Guardrails and security tools to secure the model
9. Monitor, Optimize, and Improve AI Agents
- Track AI performance using key metrics like efficiency, accuracy and response time.
- Collect user feedback to identify areas for improvement.
- Update and fine-tune AI models regularly to improve accuracy and relevance.
- Monitor Model Drifts.
- Stay updated on industry developments and emerging AI advancements.
- Monitor new technologies, updates, and improvements in AI models.
- Adapt to changes by integrating relevant upgrades into existing AI systems.
- Continuously evaluate and refine AI strategies based on industry trends.
- Test AI in different scenarios to ensure adaptability and reliability.
10. Scale AI Across the Organization
- Expand AI use from one function to multiple business areas.
- Deploy AI agents that collaborate across departments.
- Use AI-driven insights for strategic business planning.
- Automate more complex workflows as AI capabilities improve.
- Share case studies across teams.
What world leaders are saying about AI agents?
-
Sam Altman, CEO of OpenAI (ChatGPT) said “AI Agents Set to Join the Workforce by 2025”
-
Sundar Pichai, CEO of Alphabet, emphasized AI's profound impact, stating, "AI is the biggest technological shift of our lifetimes."
-
Elon Musk, CEO of Tesla and SpaceX said "The clock is ticking—AI agents are not just a trend; they are the future of efficiency and innovation."
-
Satya Nadella, CEO of Microsoft said “AI agents will become the primary way we interact with computers in the future. They will be able to understand our needs and preferences, and proactively help us with tasks and decision-making."
What are some real-world case studies of AI agents?
1. Personalized Healthcare
- Diagnostics and Treatment Agentic AI improves healthcare outcomes through personalized treatment recommendations, real-time condition monitoring, and timely interventions. Companies like Tempus Labs, Philips, Google, and IBM have invested in AI agent development for healthcare.
- Cancer Detection The U.S. Dept. of Veterans Affairs is using AI at the edge via an Augmented Reality Microscope (ARM) to improve cancer detection for service members and veterans at remote military treatment facilities.
2. Customer Service
- 24/7 Support AI-powered chatbots offer round-the-clock support, addressing routine inquiries and escalating complex issues to human agents.
- Telecom Italia (TIM) Implemented a Google-powered voice agent to handle many customer calls, increasing efficiency by 20%.
- Elisa A telecom company, developed a chatbot named Annika, which handled over 560,000 client interactions, resolving numerous customer contacts and saving significant operational time.
3. E-commerce and Retail
- Personalized Recommendations AI agents provide personalized beauty advice and suggest ideal product matches. Olay's Skin Advisor and Sephora's Pocket Contour are examples of brands using AI to offer tailored recommendations.
- Snap Has deployed the multimodal capability of Gemini within its “My AI” chatbot and has since seen over 2.5-times as much engagement within Snapping to My AI in the United States.
4. Financial Services
- Fraud Detection Agentic AI monitors network traffic and detects anomalies, helping organizations protect data by blocking suspicious transactions and isolating compromised systems. PayPal, Cisco, and Darktrace are examples of companies using AI for cybersecurity.
- Commerzbank A leading German bank, implemented an AI agent powered by Gemini 1.5 Pro to automate the documentation of client calls, freeing up its financial advisors from tedious manual processes.
- Banestes A Brazilian bank, used Gemini in Google Workspace to streamline work dynamics, such as accelerating credit analysis by simplifying balance sheet reviews and boosting productivity in marketing and legal departments.
- Discover Financial Helps its 10,000 contact center representatives to search and synthesize information across detailed policies and procedures during calls.
- Five Sigma Created an AI engine which frees up human claims handlers to focus on areas where a human touch is valuable, like complex decision-making and empathic customer service.
5. Marketing and Advertising
- Dynamic Ad Personalization Agentic AI runs personalized advertisements in real-time, adjusting ad content and bidding strategies based on user behavior and demographics. Netflix, Spotify, Salesforce, and Cognitiv are examples.
6. Logistics and Supply Chain
- Optimization Agentic AI optimizes supply chains by predicting demand, managing inventory, and adjusting procurement strategies. FedEx utilizes AI for intelligent logistics management, optimizing routes and inventory levels.
- Amazon Has transformed its supply chain into a highly responsive and efficient system using AI-driven predictive analytics, optimizing inventory and reducing operational costs.
7. Government
- New York State Department of Motor Vehicles Is transforming the driver service experience with AI to enable greater efficiency and accessibility within the DMV, directly benefiting the public it serves.
- Sullivan County, New York Is utilizing gen AI to enhance citizen interactions. The bot empowers residents with increased transparency and direct communication.
- U.S. Patent and Trademark Office Has improved the quality and efficiency of its patent and trademark examination process by implementing AI-driven technologies.
8. Business Operations
- Meeting Scheduling Pragmatic, an AI strategy consulting firm, leveraged Lindy to automate their meeting scheduling processes.
- Email Negotiation Tiddle, an influencer agency, integrated Lindy to automate their email negotiation processes.
What is the future of AI agents?
1. Enhanced Reasoning and Task Handling
- AI agents will exhibit improved reasoning via large language models (LLMs), enabling them to analyze complex scenarios and provide nuanced explanations. They will also be capable of breaking down and executing multi-step tasks, previously unattainable for AI.
2. API Interactions
- AI agents will be able to interact with external tools and APIs, accessing real-time data and controlling other software to perform tasks like scheduling appointments or ordering groceries.
3. Multi-Agent Systems
- Multi-agent systems will take center stage, moving beyond single-agent applications to tackle high-impact challenges requiring multiple business disciplines. These systems will collaborate, adapt, and execute, enabling enterprises to solve complex problems.
4. Agent Orchestration
- To manage AI labor effectively, "chief-of-staff" agents may emerge to oversee other agents and ensure human control over AI systems.
5. Autonomous DevOps
- AI agents will manage infrastructure provisioning, scaling, and monitoring, paving the way for self-operating clouds.
6. Hyper-Personalization
- Agents will enable the creation of highly customized software tailored to individual user needs.
7. AI-First Architectures
- Applications will be designed with agents as primary actors, orchestrating workflows, interactions, and decisions.
8. Real-Time Collaboration
- Agent-driven development will facilitate real-time collaboration, allowing globally distributed teams to work seamlessly across time zones and languages.
9. Self-Healing Systems
- AI agents will monitor systems, identify issues, generate patches, and deploy fixes autonomously, minimizing downtime and enhancing reliability.
10. Democratization of Development
- Agent-driven paradigms will enable non-developers to build applications, lowering the barrier to entry.
Conclusion
- AI agents are transforming industries by automating tasks, optimizing decision-making, and enhancing efficiency. From healthcare and finance to retail and manufacturing, these intelligent systems are driving innovation and reshaping business operations. As AI continues to evolve, future AI agents will become more autonomous, adaptive, and capable of human-like reasoning, unlocking new opportunities for businesses and society. However, challenges like bias, security risks, and ethical concerns must be addressed to ensure responsible AI development. Companies that embrace AI agents today will gain a competitive edge, paving the way for a smarter, more automated future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are What Are AI Agents? More Than Just Chatbots?
What Are AI Agents? More Than Just Chatbots are AI-powered systems that automate and optimize processes using machine learning, natural language processing, and intelligent decision-making capabilities.
How do What Are AI Agents? More Than Just Chatbots work?
What Are AI Agents? More Than Just Chatbots work by analyzing data, learning patterns, and executing tasks autonomously while integrating with existing systems to streamline operations and improve efficiency.
What are the benefits of using What Are AI Agents? More Than Just Chatbots?
The benefits include increased efficiency, reduced operational costs, improved accuracy, 24/7 availability, better customer experience, and data-driven insights for decision-making.


















