Why Companies Need a Microservices Architecture
Introduction
- The lending industry contributes to the economy by facilitating economic growth and financial stability. By providing loans, individuals and businesses can pursue personal and entrepreneurial opportunities, leading to job creation and increased financial stability. This industry also supports investment in infrastructure projects, such as new construction and the expansion of existing businesses.
How Lending Is Becoming More Digital
-
The lending industry is rapidly embracing digital transformation, revolutionizing the way loans are originated, processed, and serviced. With the rise of digital platforms and technologies, borrowers can now apply for loans online, often through user-friendly interfaces and mobile applications, eliminating the need for traditional paper-based applications. Moreover, lenders are leveraging data analytics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning algorithms to automate credit scoring and underwriting processes, enabling faster decision-making and more accurate risk assessment. Digitalization also facilitates seamless communication between lenders and borrowers, allowing for real-time updates on loan status, document submission, and account management. As a result, digital lending offers greater convenience, accessibility, and efficiency for both borrowers and lenders, driving the industry towards a more streamlined and customer-centric future.
-
Proper digital infrastructure is indispensable in today's interconnected world, serving as the backbone for seamless communication, data exchange, and technological innovation. From businesses and governments to individuals, a robust digital infrastructure is essential for enabling economic growth, enhancing productivity, and fostering innovation. With the increasing reliance on digital technologies across various sectors, including finance, healthcare, education, and transportation, the need for reliable internet connectivity, secure data storage, and interoperable systems has never been greater. Moreover, digital infrastructure plays a crucial role in bridging the digital divide, ensuring that all individuals have access to essential services and opportunities in the digital age.
The Need For Microservices Architecture
1.Faster Development and Deployment
- Imagine independent, self-contained units instead of a cumbersome giant. Microservices break down monolithic applications into smaller, autonomous services, each focused on a specific functionality. This enables developers to work independently, leading to faster development cycles and quicker deployments. Updates and fixes become isolated events, minimizing downtime and risk across the entire application.in this way Microservices architecture can help in faster development and deployment.
2.Enhanced Scalability
- Need to cater to sudden spikes in user traffic? With microservices, you can scale individual services up or down based on demand, ensuring optimal performance without straining the entire system. This elasticity allows businesses to cater to fluctuating needs efficiently and cost-effectively. in this way Microservices architecture can enhance the scalability.
3.Improved Fault Tolerance:
- A single bug in a monolithic application can bring everything down. But with microservices, failure in one service is contained, preventing it from cascading and impacting other functionalities. This resilience ensures consistent uptime and user experience, even if issues arise in specific areas. in this way Microservices architecture can improve fault tolerance.
4.Technology Agnostic
- No longer beholden to a single technology stack, microservices allow you to choose the best tools for each specific functionality. This freedom fosters innovation and enables the adoption of emerging technologies without rewrites or major architectural changes.
5.Continuous Integration and Deployment
- CI/CD practices become seamless with microservices. Smaller, independent units facilitate automated testing and deployment, resulting in faster feedback loops and quicker response to changing market demands. in this way Microservices architecture can help in continuous integration and deployment.
6.Team Autonomy and Ownership
-
Each microservice can be owned and developed by a dedicated team, fostering ownership, accountability, and improved developer experience. This leads to increased motivation and a culture of continuous improvement. in this way Microservices architecture can help in development.
-
In India, NBFC and Banking institutions are allowed to lend money to customers. Digital Lending is now normal. There are lots of APIs available to check various aspects of customers. Dirsurbments can happen within minutes instead of days.
-
Technology innovation in Digital APIs, Regulatory Support and AI has demanded much more robust, secure and scalable infrastructure.
-
Monolithic Architecture is becoming a legacy in modern infrastructure.
-
We are presenting a Microservices Architecture.
Comparison of monolithics architecture and Microservices architecture
- Monolithic architecture is a classic strategy in which all application components are closely connected and delivered together. This implies that changing or updating one component may need redeploying the entire programme. Microservice architecture, on the other hand, is a new method that breaks down an application into a series of loosely connected services, each of which is responsible for a single purpose. Microservices architecture services may be built, launched, and expanded separately, providing more flexibility and resilience. While monolithic design may be easier to create and test, microservice architecture has benefits such as improved scalability, maintainability, and the ability to readily embrace new technologies. However, it increases complexity in terms of deployment, monitoring, and inter-service communication.
Microservices Lending Architecture
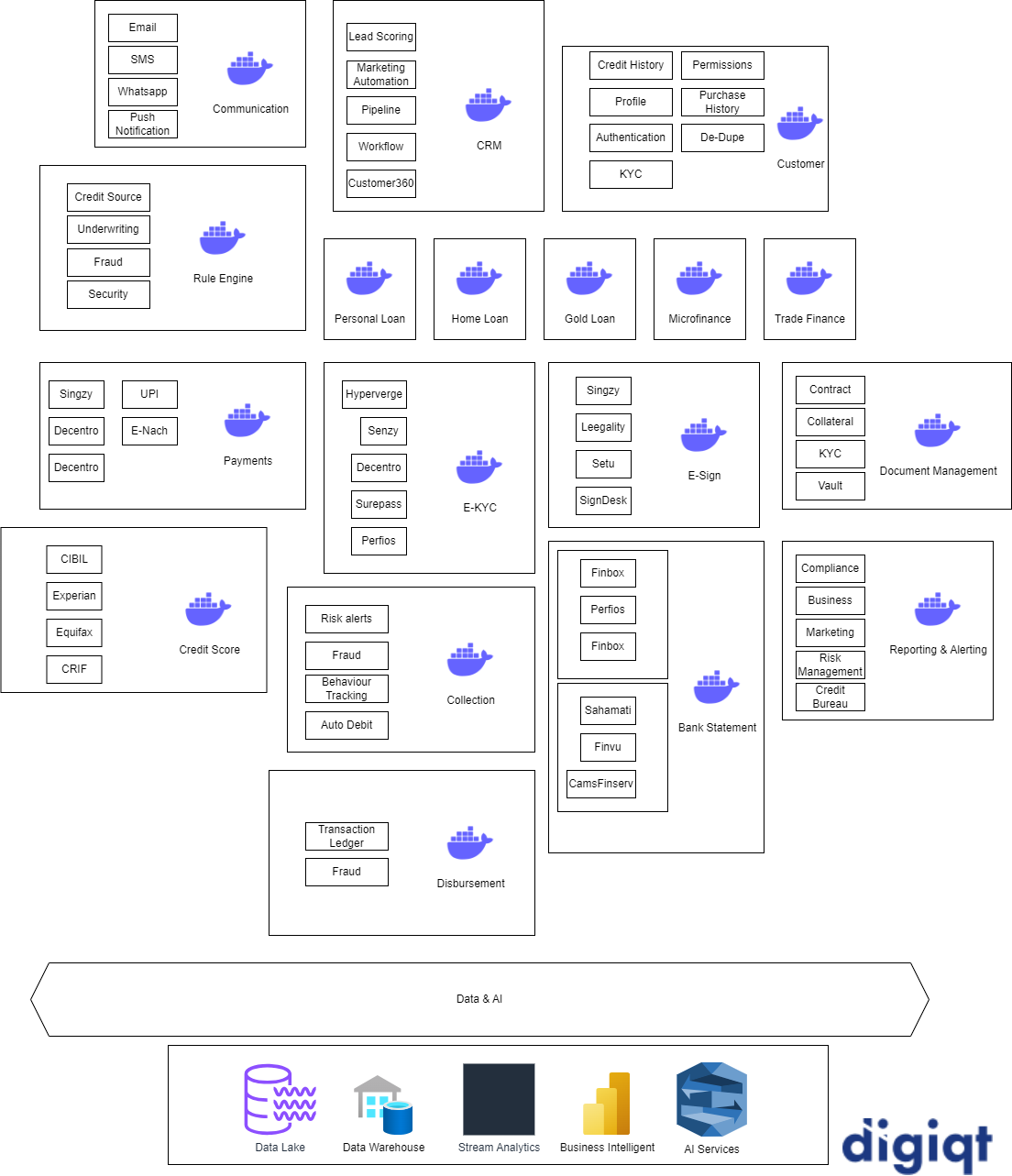
- Architecture has various microservices designed to function in Digital Lending journeys. These microservices can be further divided into microservices based on the scale and requirements.
1. CRM
-
A Customer Relationship Management (CRM) microservice is a small, independent, and modular service that focuses on managing and optimizing interactions between a company and its customers. In a microservices architecture, CRM functionalities can be broken down into separate microservices, each responsible for specific aspects of customer management, ensuring scalability, flexibility, and maintainability.
-
CRM Microservice includes Customer Lead Management, Workflows, Lead Scores, PIpelines, Tasks, Activity Tracking, Funnel, Customer 360 etc.
2. Customer
- Customer microservices play a crucial role in putting all customer data at single place. It stores Customer Credit History, Profile, Permissions, KYC and Authentication details. This service helps in Customer Authentication, Customer history, persona, De-Dupe and Fraud Detection.
3. Personal, Home, Gold, Microfinance, Trade Finance Loans (LoS)
- This is a critical component in the lending process, providing financial institutions with the tools to manage and streamline the end-to-end process of originating, underwriting, and disbursing loans. LOS plays a pivotal role in different types of loans, each with its specific requirements and workflows.
4. Rule Engine
- A Rule Engine microservice in lending is a crucial component that leverages business rules to automate decision-making processes within the loan origination and management lifecycle. It plays a pivotal role in ensuring consistency, compliance, and efficiency by applying predefined rules to evaluate loan applications, determine eligibility, and manage various aspects of the lending process. Modern Rule Engines are equipped with AI engines which can help companies to auto-identify the gaps in rules and find the inter-connected effects of various rules that are not possible for humans to identify.
5. Communication
- A Communication Microservice is a vital component within a larger software ecosystem that handles various communication channels such as WhatsApp, SMS, email, and other forms of communication. Its primary objective is to streamline and centralize the sending and receiving of messages, ensuring consistent and efficient communication with users or customers. Such a service centralizes all the communication across all the infrastructure. Centralized monitoring, validation and logic can be implemented in this service without affecting other services.
6. Payments
- A Payments Microservice within a lending company is a specialized component which takes care of cross payment gateway, E-Nach, UPI etc integrations for LoS. This service can lead to re-usability of integrations across the infrastructure. For example, if Gold loan is using Payment Gateway 1 and Microfinance journey is using payment gateway 2. Now, in future some other lending journey is using payment gateway 1 or 2, such integration time can be saved by using the payments microservices.
7. Credit Score
- A Credit Score Microservice in lending is a specialized component that assesses and manages the creditworthiness of loan applicants. It plays a crucial role in the loan origination process by providing insights into an individual's or a business's credit history, financial behavior, and overall risk profile. This microservice can have centralized pre and post-processing logic for credit scores. Just like payment services existing integrations can be re-used.
8. E-KYC
- An e-KYC (Electronic Know Your Customer) Microservice in lending is a specialized component that leverages digital technologies to automate and streamline the customer onboarding process. The primary objective of the e-KYC Microservice is to verify the identity of loan applicants electronically, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and enhancing the efficiency of the Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures.
9. Disbursement
- A Disbursement Microservice in lending is a specialized component that manages the efficient and secure distribution of funds to borrowers upon loan approval. It plays a crucial role in the final stages of the loan origination process, ensuring that approved loan amounts are disbursed accurately and promptly. This service also maintains a secure ledger of accounts.
10. Collection
- A Collection Microservice in lending is a specialized component that manages the process of collecting repayments from borrowers. It plays a critical role in the post-disbursement phase of the lending lifecycle, ensuring that borrowers fulfill their repayment obligations according to the terms and conditions of their loans. Service also includes Customer monitoring & risk alerts, fraud, customer behavior tracking and auto debit.
11. E-Sign
- An E-signature (Electronic Signature) Microservice in lending is a specialized component that facilitates the electronic signing of loan documents and agreements. It plays a crucial role in the digitization of the loan origination process, allowing borrowers and other parties involved to sign documents securely and efficiently.
12. Bank Statement
- A Bank Statement Microservice in lending is a specialized component that facilitates the retrieval, processing, and analysis of bank statements as part of the loan application and approval process. It plays a crucial role in assessing the financial health and creditworthiness of loan applicants by analyzing their transaction history and financial behaviors. This service can also integrated with Account Aggregation frameworks. Service will also include analyzing the bank statements with OCR. Service can also perform the pattern identification and technical analysis of bank statements for loan eligibility of customers. Modern microservices also leverage AI to scan bank statements.
13. Document Management
- A Document Management Microservice in lending is a specialized component that handles the organization, storage, retrieval, and processing of various documents and files throughout the loan lifecycle. It plays a pivotal role in digitizing and streamlining the document-intensive processes associated with loan origination, underwriting, and servicing. Such a service also encrypts the documents either with encryption keys or hardware Vault-based security.
14. Reporting & Alerting
- A Reporting and Alerting Microservice in lending is a specialized component that handles the generation of reports, analytics, and notifications to support decision-making, regulatory compliance, and risk management within the lending ecosystem. This microservice is essential for monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs), identifying trends, and proactively addressing potential issues.
15. Data Lake
- A Data Lake is a centralized repository that allows organizations to store vast amounts of raw and unstructured data at scale. It provides a flexible and cost-effective solution for collecting, storing, and processing diverse data types, enabling advanced analytics, machine learning, and data exploration. Data Lakes offer a unified storage infrastructure, fostering collaboration and facilitating data-driven decision-making across an organization.
16. Data Warehouse
- A Data Warehouse is a centralized repository that aggregates and organizes structured data from various sources, providing a platform for business intelligence and analytics. It is optimized for fast and efficient querying, allowing users to analyze historical and current data to gain insights into business performance. Data Warehouses play a crucial role in decision support systems, offering a consolidated and structured view of data for strategic decision-making.
17. Steam Analytics
- Stream Analytics is a real-time data processing technology that analyzes and derives insights from continuous streams of data. It enables organizations to process, filter, and extract valuable information from live data sources, such as customer behavior, sales, transactions or any other event streams. Stream Analytics is crucial for making instant, data-driven decisions and responding swiftly to dynamic scenarios in various industries.
18. Business Intelligence
- Business Intelligence (BI) is a technology-driven process for analyzing and visualizing business data to make informed decisions. It involves collecting, transforming, and presenting data insights, helping organizations gain a comprehensive understanding of their performance and trends. BI tools empower users to create reports, dashboards, and interactive visualizations for strategic decision-making across various business functions.
19. AI Services
-
AI services on top of a data lake in lending leverage machine learning algorithms to extract valuable insights and predictions from vast and diverse datasets. These services analyze transaction histories, customer behaviors, and credit data in real-time, aiding in risk assessment, fraud detection, and personalized lending strategies. By integrating AI on a data lake, lending institutions can enhance decision-making processes, optimize loan portfolios, and provide more tailored and responsive financial solutions to their customers.
-
There can be more microservices added based on the company structure.
Technical Architecture
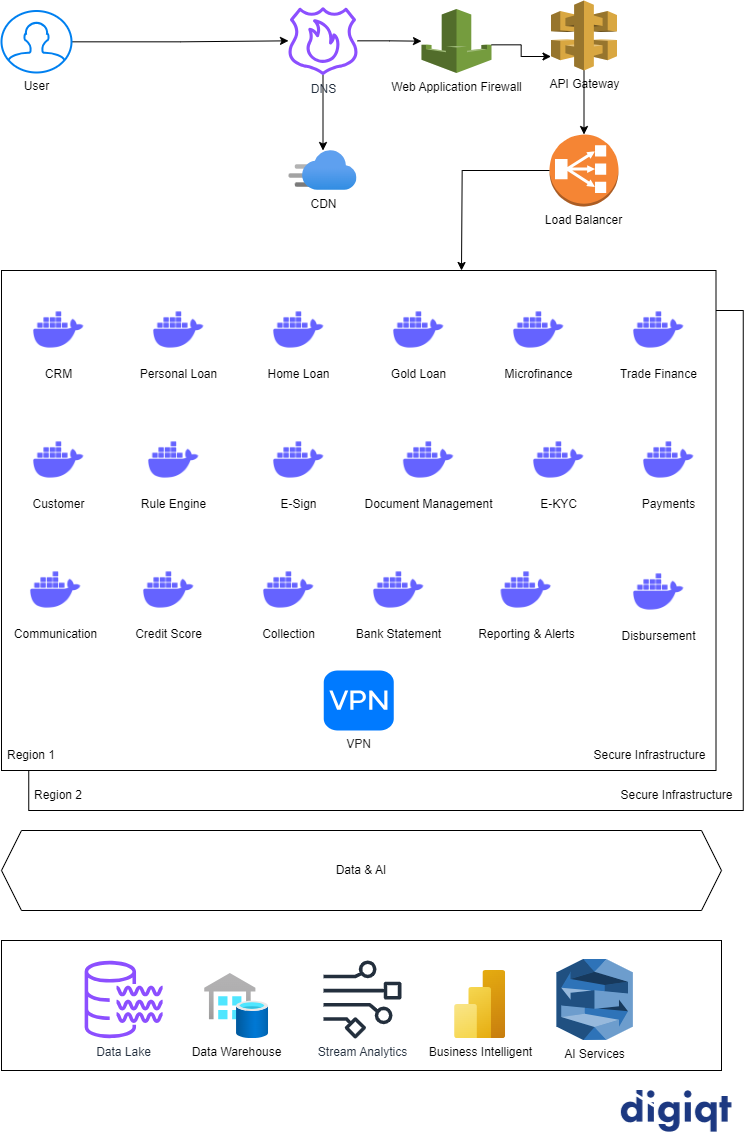
1. DNS
-
DNS, or Domain Name System, is a hierarchical decentralized system that translates human-readable domain names into numerical IP addresses, facilitating internet communication. It plays a critical role in mapping user-friendly domain names to the corresponding IP addresses, enabling users to access websites and services using memorable names instead of numerical IP addresses. DNS operates as a distributed network of servers, ensuring efficient and reliable resolution of domain names across the internet.
-
In case of Disaster Recovery, DNS can also switch to a different infrastructure.
2. CDN
-
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a distributed network of servers strategically placed around the world to optimize the delivery of web content. By caching and delivering content from servers located closer to end-users, CDNs enhance website performance, reduce latency, and improve overall user experience. This geographically dispersed infrastructure accelerates content delivery, ensuring faster loading times and increased reliability for websites and online applications.
-
As a best practice all the static content such as, images, videos, gifs, public pdfs etc are hosted on CDN for better performance.
3. WAF
- A Web Application Firewall (WAF) is a security solution that protects web applications from various online threats and vulnerabilities. It monitors, filters, and blocks malicious traffic to prevent unauthorized access, injection attacks, and other cyber threats, enhancing the security of web applications. WAFs play a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive data and ensuring the integrity of web-based systems.
4. API Gateway
- An API Gateway is a centralized entry point that manages and orchestrates interactions between microservices and external clients in a distributed system. It acts as a gatekeeper, handling authentication, authorization, request routing, and traffic management, simplifying the complexities of API management. API Gateways enhance security, scalability, and maintainability in microservices architectures by providing a unified interface for communication.
5. Load Balancer
- A Load Balancer is a networking device that distributes incoming traffic across multiple servers to ensure optimal resource utilization, prevent server overload, and enhance system reliability. It improves the performance and availability of applications by evenly distributing workloads and seamlessly redirecting traffic in case of server failures. Load Balancers play a crucial role in scaling and maintaining the stability of web services, applications, and server clusters.
6. VPN
-
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a secure and encrypted connection that allows users to access a private network over the internet, ensuring privacy and data security. VPNs are commonly used for remote work, providing a secure tunnel for users to connect to corporate networks from any location and protecting sensitive information from potential threats. By masking IP addresses and encrypting data, VPNs enhance online privacy and safeguard communication in both personal and business contexts.
-
There can be multiple other microservice components such as, Service Registry, Orchestration, Centralized Configuration, Monitoring and Logging, Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment etc.
Conclusion
-
In the Microservices Lending Architecture, various specialized microservices are designed to streamline Digital Lending journeys. These microservices, including CRM, Customer, Loans (LoS), Rule Engine, Communication, Payments, Credit Score, E-KYC, Disbursement, Collection, E-Sign, Bank Statement, Document Management, Reporting & Alerting, Data Lake, Data Warehouse, Stream Analytics, Business Intelligence, and AI Services, collectively contribute to a modular, scalable, and efficient lending ecosystem.
-
The CRM Microservice focuses on optimizing customer interactions, while the Customer Microservice consolidates all customer data. The Loans (LoS) Microservice manages diverse lending types, and the Rule Engine automates decision-making with predefined rules. Communication Microservice centralizes communication channels, Payments Microservice integrates cross-gateway transactions, and Credit Score Microservice assesses creditworthiness. E-KYC, Disbursement, Collection, E-Sign, Bank Statement, and Document Management microservices handle specific lending processes. Reporting & Alerting Microservice aids decision-making, and the Data Lake, Data Warehouse, Stream Analytics, Business Intelligence, and AI Services leverage data for advanced analytics and insights.
-
This architecture also incorporates essential components like DNS, CDN, WAF, API Gateway, Load Balancer, and VPN for security, performance, and networking. Overall, this comprehensive Microservices Lending Architecture enables a responsive, adaptable, and data-driven approach to lending operations.
Contact Us
Frequently Asked Questions
What are Why Companies Need a Microservices Architecture?
Why Companies Need a Microservices Architecture are AI-powered systems that automate and optimize processes using machine learning, natural language processing, and intelligent decision-making capabilities.
How do Why Companies Need a Microservices Architecture work?
Why Companies Need a Microservices Architecture work by analyzing data, learning patterns, and executing tasks autonomously while integrating with existing systems to streamline operations and improve efficiency.
What are the benefits of using Why Companies Need a Microservices Architecture?
The benefits include increased efficiency, reduced operational costs, improved accuracy, 24/7 availability, better customer experience, and data-driven insights for decision-making.
















